Concepts in Database
This part introduces essential ideas that form the foundation of database management. Databases organize and store information efficiently, making it easier to access and manipulate data in various applications.
Table¶
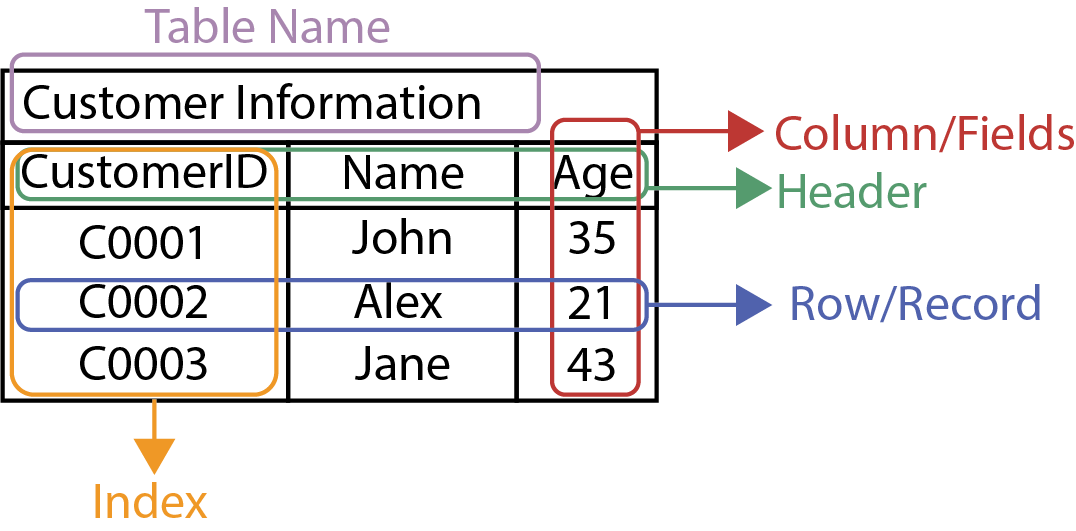
Table structure with rows, columns, index, header, and table name.
A table is a structured collection of information arranged into rows and columns. Each row represents an individual record, while each column holds specific details concerning the record. In many cases, the first column serves as an index, which helps in locating data quickly without having to search the entire table. Headers are used to label each column, providing context for the data stored in the table. The table name is used to identify the table and distinguish it from other tables in the database.
Index and Indexing¶

Index and indexing concept in databases: You can find the index at the end of a book (left panel), which helps in locating specific information quickly. Search engines (right panel) also use indexing to speed up the process of retrieving web pages.
An index is a copy of selected columns designed to speed up the process of retrieving data. Indexing involves analyzing data and storing it in a way that makes subsequent searches faster. In a similar manner to how search engines index web pages using crawlers, databases create indexes to enhance query performance. This approach prevents the need to scan every row in a table, which is especially useful in large datasets.
Key and Value¶
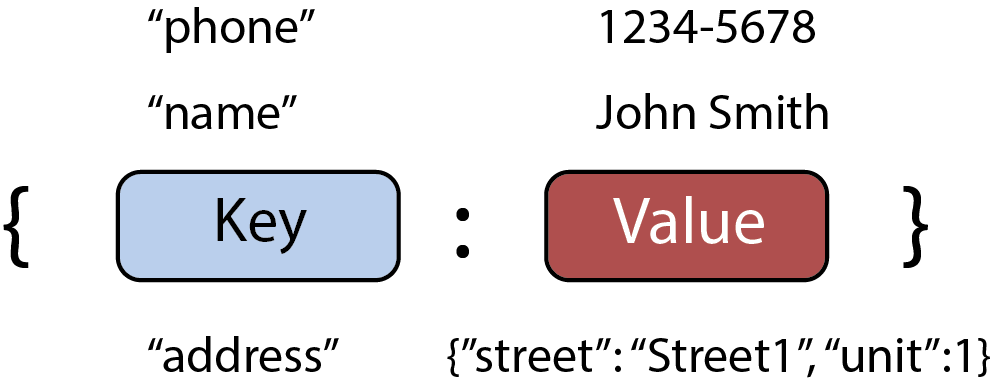
Key-value pairs in a database: Each key is associated with a value, similar to a dictionary in Python.
The key and value concept is central to many data structures, including databases and dictionaries in programming languages like Python. Here, a key uniquely identifies a piece of data, and the value is the data associated with that key. For example, a Python dictionary stores data in the format {key: value}. The use of hashing in these structures makes data lookup very efficient, typically achieving a time complexity of O(1), which indicates a constant time operation regardless of the data size.
Data Query¶
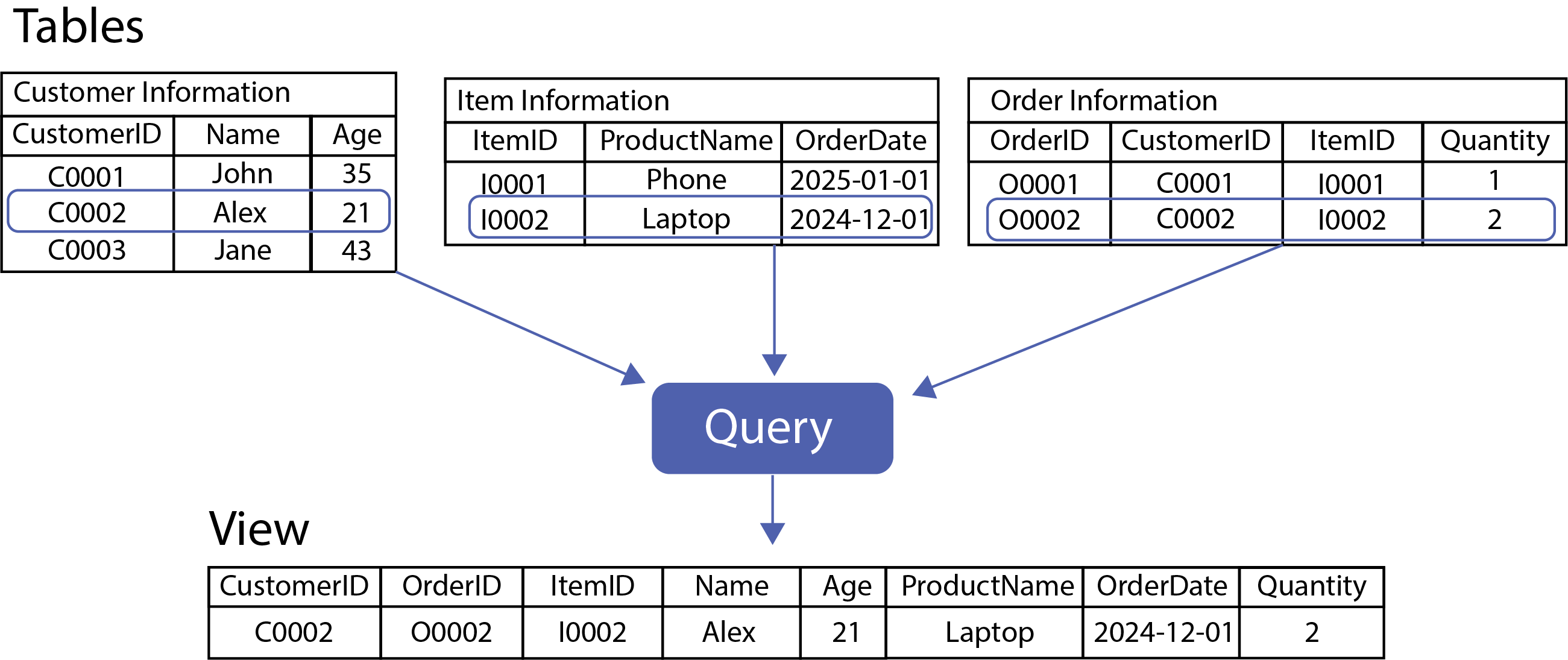
Database query: A query is a set of instructions given to a database to retrieve or update data. The retrieved data is shown as view.
A query is a series of instructions given to a database to retrieve or update data. SQL is the most commonly used language for writing queries. One frequently used SQL command is the SELECT statement, which fetches data from one or more tables. When a query runs, the database processes the instructions and returns a set of results based on the specified conditions.
For example, in the figure above, if we want to retrieve the customer information for an individual named “Alex,” we would write a query like SELECT * FROM customers WHERE Name = 'Alex'. The database then returns the relevant information about the customer. Queries can also combine data from multiple tables using JOIN operations.