Practical: Bulk Modulus
Introdction¶
Bulk modulus is a measure of how resistant a material is to compression. It is defined as the ratio of the infinitesimal pressure increase to the resulting relative decrease of the volume.
where is the bulk modulus, is the volume, is the pressure, and is the total energy.
Relationship Between Bulk Modulus and Density¶
Like Young’s modulus, typically, the bulk modulus of a material is positively related to its density. For example, gases have low bulk moduli and low density because they are easily compressed, while solids have high bulk moduli with higher density because they are more difficult to compress. This is because the bulk modulus is a measure of how resistant a material is to compression, and denser materials are generally more resistant to compression.
VRH, Reuss, and Hill Averages¶
There are different ways to measure the bulk modulus. The Voigt average assumes that the strain is uniform throughout the material, which tends to overestimate the bulk modulus. The Reuss average assumes that the stress is uniform throughout the material, which tends to underestimate the bulk modulus. The Hill average, being the arithmetic mean of the Voigt and Reuss averages, provides a more accurate estimate of the bulk modulus by balancing these two extremes.
The Voigt-Reuss-Hill (VRH) average is a method for calculating the bulk modulus of a composite material. The VRH average is the arithmetic mean of the Voigt and Reuss bounds, which are upper and lower bounds on the bulk modulus of a composite material. The Hill average is a weighted average of the Voigt and Reuss bounds, with the weights determined by the volume fractions of the phases in the composite material. We will use the VRH average to calculate the bulk modulus of a material in this practical.
In Materials Project, the bulk modulus data is returned as a dictionary (bulk_modulus) with the following keys:
vrh: The VRH average of the bulk modulus. Average ofreussandvoigt.reuss: The Reuss average of the bulk modulus.reussis the lower bound of the bulk modulus.voigt: The Voigt average of the bulk modulus.voigtis the upper bound of the bulk modulus.
# you can skip this if you've already installed the mp_api package.
!pip install mp_apiMP_API_KEY = "your-key" # You can get your API key at https://next-gen.materialsproject.org/dashboard
from mp_api.client import MPRester
# Pass your API key directly as an argument.
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "volume","density", "bulk_modulus", "shear_modulus"], is_stable=True, k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 5161/5161 [00:03<00:00, 1389.38it/s]
# dump results to a json file
import json
with open('materials_data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs], f, indent=4)We can then load the saved data and construct a DataFrame for easier manipulation.
import pandas as pd
# load results from a json file as pandas dataframe
df = pd.read_json('materials_data.json')[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus', 'shear_modulus']]
print(df) material_id volume density \
0 mp-861724 110.157369 11.367264
1 mp-862319 135.917612 8.370293
2 mp-862786 113.979079 8.598305
3 mp-861883 104.095515 11.322190
4 mp-865470 126.204675 8.371544
... ... ... ...
5156 mp-2979 182.235382 6.052680
5157 mp-4524 158.907389 4.179819
5158 mp-429 46.275258 8.906569
5159 mp-11621 50.980115 8.008301
5160 mp-11025 470.143187 3.598571
bulk_modulus \
0 {'voigt': 67.493, 'reuss': 67.493, 'vrh': 67.493}
1 {'voigt': 42.615, 'reuss': 42.615, 'vrh': 42.615}
2 {'voigt': 54.864, 'reuss': 54.864, 'vrh': 54.864}
3 {'voigt': 68.935, 'reuss': 68.935, 'vrh': 68.935}
4 {'voigt': 46.296, 'reuss': 46.296, 'vrh': 46.296}
... ...
5156 {'voigt': 161.892, 'reuss': 161.782, 'vrh': 16...
5157 {'voigt': 73.52, 'reuss': 73.511, 'vrh': 73.515}
5158 {'voigt': 144.716, 'reuss': 144.674, 'vrh': 14...
5159 {'voigt': 96.917, 'reuss': 96.917, 'vrh': 96.917}
5160 {'voigt': 68.456, 'reuss': 68.431, 'vrh': 68.444}
shear_modulus
0 {'voigt': 17.02, 'reuss': 12.045, 'vrh': 14.533}
1 {'voigt': 18.924, 'reuss': 14.148, 'vrh': 16.536}
2 {'voigt': 19.247, 'reuss': 18.973, 'vrh': 19.11}
3 {'voigt': 20.551, 'reuss': 15.647, 'vrh': 18.099}
4 {'voigt': 13.564, 'reuss': 13.564, 'vrh': 13.564}
... ...
5156 {'voigt': 96.845, 'reuss': 94.023, 'vrh': 95.434}
5157 {'voigt': 51.337, 'reuss': 47.084, 'vrh': 49.211}
5158 {'voigt': 72.993, 'reuss': 51.411, 'vrh': 62.202}
5159 {'voigt': 40.42, 'reuss': 39.729, 'vrh': 40.075}
5160 {'voigt': 43.377, 'reuss': 41.658, 'vrh': 42.518}
[5161 rows x 5 columns]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Extract 'vrh' values from 'bulk_modulus' dictionaries
df['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'])
df['shear_modulus_vrh'] = df['shear_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'])
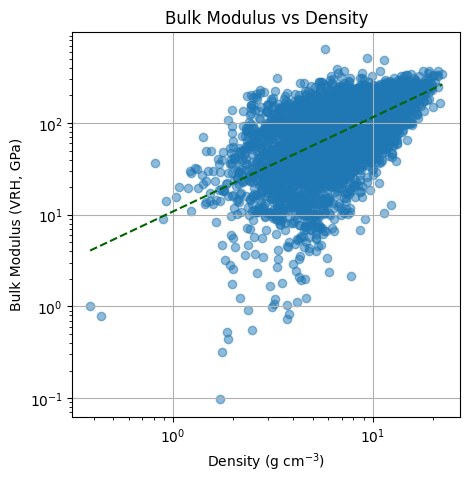
# Plot bulk modulus vs density
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.title('Bulk Modulus vs Density')
plt.xlabel('Density (g cm$^{-3}$)')
plt.ylabel('Bulk Modulus (VRH, GPa)')
plt.grid(True)
# Fit linear trend line in log-log space
log_density = np.log(df['density'])
log_bulk_modulus = np.log(df['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
# Fit linear trend line in log-log space
slope, intercept = np.polyfit(log_density, log_bulk_modulus, 1)
# Plot trend line
x = np.linspace(df['density'].min(), df['density'].max(), 100)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept) * x**slope, color='darkgreen', linestyle='--')
print(f'Trend line: y = {np.exp(intercept):.2f} * x^{slope:.2f}')
# Plot filtered data
plt.scatter(df['density'], df['bulk_modulus_vrh'], alpha=0.5)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()
Trend line: y = 10.87 * x^1.03
print(f"K = {slope:.2f} * density * exp({intercept:.2f})")
print(f"Cu: prediction = {slope*8.96*np.exp(intercept):.1f} GPa and experimental value 140 GPa")
print(f"Fe: prediction = {slope*7.87*np.exp(intercept):.1f} GPa and experimental value 170 GPa")
print(f"Ag: prediction = {slope*10.49*np.exp(intercept):.1f} GPa and experimental value 100 GPa")
print(f"Al: prediction = {slope*2.67*np.exp(intercept):.1f} GPa and experimental value 76 GPa")
K = 1.03 * density * exp(2.39)
Cu: prediction = 100.0 GPa and experimental value 140 GPa
Fe: prediction = 87.9 GPa and experimental value 170 GPa
Ag: prediction = 117.1 GPa and experimental value 100 GPa
Al: prediction = 29.8 GPa and experimental value 76 GPa
Visualize the Distribution of Bulk Modulus and Density¶
Bar plots
# Plot distribution of density
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.hist(df['density'], bins=30, color='blue', alpha=0.7)
plt.title('Density Distribution')
plt.xlabel('Density (g cm$^{-3}$)')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
# Plot distribution of bulk modulus
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist(df['bulk_modulus_vrh'], bins=30, color='green', alpha=0.7)
plt.title('Bulk Modulus Distribution')
plt.xlabel('Bulk Modulus (VRH, GPa)')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()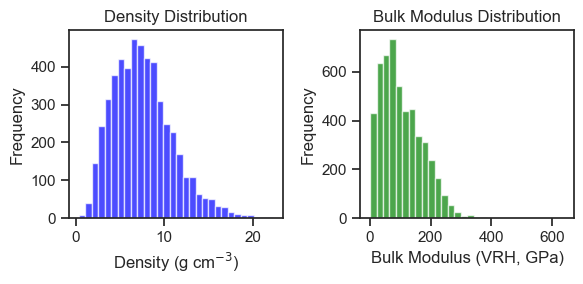
We can also use seaborn to visualize the distribution of bulk modulus and density using the joint plot.
!pip install seabornimport seaborn as sns
# visualize above code using joint hexbin plot from seaborn
# Create a joint hexbin plot
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")
plot = sns.jointplot(x='density', y='bulk_modulus_vrh', data=df, kind='hex', gridsize=50, color="#4CB391")
plot.ax_marg_x.set_xlim(0, 20)
plot.ax_marg_y.set_ylim(0, 400)
plt.show()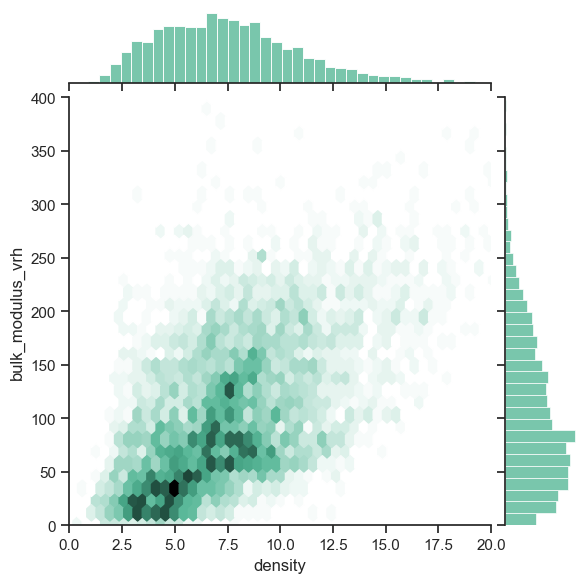
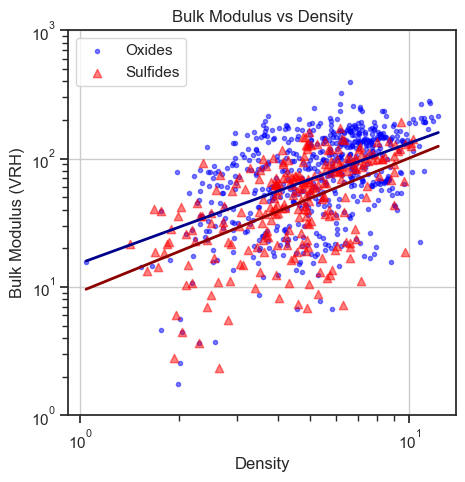
Bulk Modulus of Oxides and Sulfides¶
Usually oxides are stiff and have high bulk modulus, while sulfides are soft and have low bulk modulus. We can check this trend by plotting the bulk modulus of oxides and sulfides.
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs_oxide = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "density", "bulk_modulus"], is_stable=True, elements=[ "O"], k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs_sulfide = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "density", "bulk_modulus"], is_stable=True, elements=[ "S"], k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)
with open('materials_data_oxides.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs_oxide], f, indent=4)
with open('materials_data_sulfides.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs_sulfide], f, indent=4)Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 606/606 [00:00<00:00, 17899635.38it/s]
Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 254/254 [00:00<00:00, 8195024.74it/s]
# load results from a json file as pandas dataframe and then plot the data with two different colors
with open('materials_data_oxides.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df_O = pd.DataFrame(data)[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus']]
with open('materials_data_sulfides.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df_S = pd.DataFrame(data)[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus']]
import numpy as np
# plot the data with two different colors
# Extract 'vrh' values from 'bulk_modulus' dictionaries for oxides and sulfides
df_O['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df_O['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'])
df_S['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df_S['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'])
# Plot bulk modulus vs density for oxides and sulfides
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.scatter(df_O['density'], df_O['bulk_modulus_vrh'], color='blue', label='Oxides',marker='.', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(df_S['density'], df_S['bulk_modulus_vrh'], color='red', label='Sulfides',marker='^', alpha=0.5)
# Fit linear trend lines in log-log space
log_density_O = np.log(df_O['density'])
log_bulk_modulus_O = np.log(df_O['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
log_density_S = np.log(df_S['density'])
log_bulk_modulus_S = np.log(df_S['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
slope_O, intercept_O = np.polyfit(log_density_O, log_bulk_modulus_O, 1)
slope_S, intercept_S = np.polyfit(log_density_S, log_bulk_modulus_S, 1)
# Plot trend lines
x = np.linspace(df_O['density'].min(), df_O['density'].max(), 100)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept_O) * x**slope_O, color='darkblue', linestyle='-', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept_S) * x**slope_S, color='darkred', linestyle='-', linewidth=2)
plt.title('Bulk Modulus vs Density')
plt.xlabel('Density')
plt.ylabel('Bulk Modulus (VRH)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.ylim(1, 1e3)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs_chloride = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "density", "bulk_modulus"], is_stable=True, elements=[ "Cl"], k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs_bromide = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "density", "bulk_modulus"], is_stable=True, elements=[ "Br"], k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)
with MPRester(MP_API_KEY) as mpr:
docs_iodide = mpr.materials.summary.search(
fields=["material_id", "density", "bulk_modulus"], is_stable=True, elements=[ "I"], k_vrh=[0.01, 1000]
)
with open('materials_data_chloride.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs_chloride], f, indent=4)
with open('materials_data_bromide.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs_bromide], f, indent=4)
with open('materials_data_iodide.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump([doc.dict() for doc in docs_iodide], f, indent=4)Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 136/136 [00:00<00:00, 3565158.40it/s]
Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 92/92 [00:00<00:00, 2180090.21it/s]
Retrieving SummaryDoc documents: 100%|██████████| 77/77 [00:00<00:00, 2018508.80it/s]
# load results from a json file as pandas dataframe and then plot the data with two different colors
with open('materials_data_chloride.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df_Cl = pd.DataFrame(data)[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus']]
with open('materials_data_bromide.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df_Br = pd.DataFrame(data)[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus']]
with open('materials_data_iodide.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df_I = pd.DataFrame(data)[['material_id', 'volume', 'density', 'bulk_modulus']]import numpy as np
# plot the data with two different colors
# Extract 'vrh' values from 'bulk_modulus' dictionaries for oxides and sulfides
df_Cl['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df_Cl['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'] if isinstance(x, dict) else None)
df_Br['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df_Br['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'] if isinstance(x, dict) else None)
df_I['bulk_modulus_vrh'] = df_I['bulk_modulus'].apply(lambda x: x['vrh'] if isinstance(x, dict) else None)
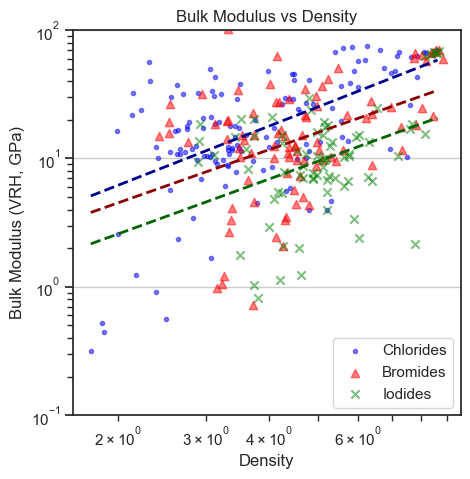
# Plot bulk modulus vs density for oxides and sulfides
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
# Fit linear trend lines in log-log space
log_density_Cl = np.log(df_Cl['density'])
log_bulk_modulus_Cl = np.log(df_Cl['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
log_density_Br = np.log(df_Br['density'])
log_bulk_modulus_Br = np.log(df_Br['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
log_density_I = np.log(df_I['density'])
log_bulk_modulus_I = np.log(df_I['bulk_modulus_vrh'])
slope_Cl, intercept_Cl = np.polyfit(log_density_Cl, log_bulk_modulus_Cl, 1)
slope_Br, intercept_Br = np.polyfit(log_density_Br, log_bulk_modulus_Br, 1)
slope_I, intercept_I = np.polyfit(log_density_I, log_bulk_modulus_I, 1)
# Plot trend lines
x = np.linspace(df_Cl['density'].min(), df_Cl['density'].max(), 100)
plt.scatter(df_Cl['density'], df_Cl['bulk_modulus_vrh'], color='blue', label='Chlorides', marker='.', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(df_Br['density'], df_Br['bulk_modulus_vrh'], color='red', label='Bromides', marker='^', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(df_I['density'], df_I['bulk_modulus_vrh'], color='green', label='Iodides', marker='x', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept_Cl) * x**slope_Cl, color='darkblue', linestyle='--', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept_Br) * x**slope_Br, color='darkred', linestyle='--', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, np.exp(intercept_I) * x**slope_I, color='darkgreen', linestyle='--', linewidth=2)
plt.title('Bulk Modulus vs Density')
plt.xlabel('Density')
plt.ylabel('Bulk Modulus (VRH, GPa)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.ylim(1e-1, 1e2)
plt.show()